Upgrading The Vial/Vein-To-Vein Process With Enterprise-Level Digital Infrastructure
By Alex Klarer, founder and managing director, Engelex
The cell and gene therapy (CGT) industry is at the forefront of medical innovation, offering the promise of curing previously untreatable diseases but is faced with a complex value chain to convert raw materials into lifesaving treatments. This value chain has come to be known as the vein-to-vein or — in the cases of iPSC-derived and viral vector therapies — vial-to-vein process for products that begin with tissue collected from a patient or volunteer donor and is infused into the patient as a live pharmaceutical product. The unique characteristics of variable inputs and the limited characterization of manufacturing processes of a nascent industry add increased difficulty to ensuring patients consistently receive a quality product. While we are progressing toward advanced analytical techniques and direct process validation, we lack the digital governance to associate critical parameters spread across the entire value chain to patient outcomes. The three main contributors, medical providers, product manufacturers, and logistics carriers, operate on isolated systems with minimal integration. Integrating these digital systems with an enterprise-level digital infrastructure can significantly improve reliability across the value chain, provide transparency for all stakeholders, and accelerate innovations in product and component characterization.
The Vial/Vein-To-Vein Process
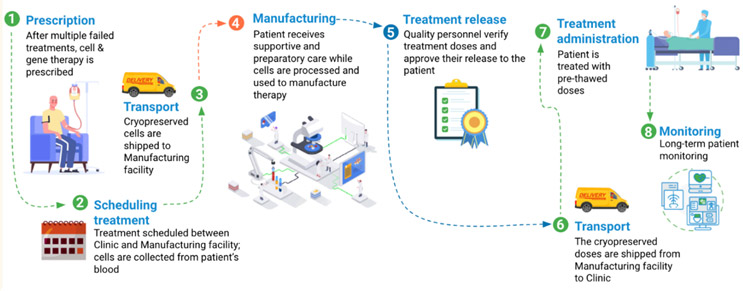
The vein-to-vein process is always evolving as new therapies and technologies are implemented. The commonly accepted definition is based on the commercialized CAR-T process; however, variations exist for allogeneic cell therapies as well as ex vivo gene therapies. For the purposes of this article, a generalized process is presented in the figure below.
Figure 1: The vial/vein-to-vein process. [Image provided with permission by Autolomous.]
Click on image to enlarge.
Each step has an impact on patient outcomes and requires meticulous coordination and precise execution to ensure the therapy's efficacy and safety. The complexity of this process is compounded by the need for real-time data tracking, stringent regulatory compliance, and the management of sensitive biologic materials.
Challenges In The Vial/Vein-to-Vein Process
- Data Management and Traceability: The vial/vein-to-vein process generates vast amounts of data, from patient information to manufacturing details and shipping information. Managing this data and ensuring its traceability is crucial for regulatory compliance and patient safety. Data presented by Accenture reenforces the point that fragmentation of digital systems across the value chain and between patients creates a significant clerical and operational burden on providers. This burden limits the rate of patient adoption and the variety of therapies offered at a given clinic.1
- Coordination and Communication: The process involves multiple stakeholders, including healthcare providers, manufacturing facilities, logistics companies, and regulatory bodies. Effective coordination and communication among these parties are essential to prevent delays and errors. However, the lack of integrated digital infrastructure can lead to miscommunication and inefficiencies.
- Quality Control and Compliance: Ensuring the quality and safety of CGT products is paramount. This requires rigorous quality control measures and adherence to regulatory standards. Manual processes and disparate systems can hinder the achievement of these goals.
The Role Of Enterprise-Level Digital Infrastructure
Enterprise-level digital infrastructure can address these challenges by providing a unified platform for managing the entire vial/vein-to-vein process. Here are some key components and benefits of such an infrastructure:
- Integrated Data Management Systems: Implementing integrated data management systems can streamline the collection, storage, and analysis of data throughout the vein-to-vein process. These systems can provide real-time visibility into each step, ensuring traceability and compliance. Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms also can be applied to identify patterns and optimize processes.
- Digital Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES): Digital MES can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of manufacturing operations. These systems can automate data capture, monitor production in real time, and ensure adherence to standard operating procedures. By integrating MES with other digital systems, manufacturers can achieve end-to-end visibility and control over the production process.
- Digital Ledger Technology: Ledger technology can be leveraged to create a secure and immutable record of each transaction and event in the vein-to-vein process. This can enhance traceability, prevent data tampering, and facilitate regulatory compliance. Digital ledgers also can enable secure sharing of data among stakeholders, fostering collaboration and transparency.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Devices: IoT devices can be used to monitor and track the condition of biological materials during transportation and storage. Sensors can provide real-time data on temperature, humidity, and other critical parameters, ensuring that the materials remain within specified conditions. This can help prevent spoilage and ensure the quality of the final product.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Cloud-based platforms can provide a scalable and flexible infrastructure for managing the vein-to-vein process. These platforms can facilitate data sharing, collaboration, and integration with other digital systems. Cloud-based solutions also can offer advanced security features to protect sensitive data.
Industry 4.0 And The Future Of CGT
The concept of Industry 4.0, characterized by the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes, is central to the future of CGT. By adopting Industry 4.0 principles, the CGT industry can achieve greater efficiency, flexibility, and innovation. Here are some ways in which implementing digital infrastructure enables the future outlook:
- Enhanced Automation and Efficiency: Industry 4.0 technologies, such as robotics and automation, can streamline the vial/vein-to-vein process, reducing manual intervention and minimizing errors. Automated systems can handle repetitive tasks with precision, freeing up human resources for more complex and value-added activities.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance: IoT devices and advanced analytics can provide real-time monitoring of equipment and processes, enabling predictive maintenance. This can help identify potential issues before they escalate, reducing downtime and ensuring the continuous operation of manufacturing facilities.
- Personalized Medicine and Customization: The digital infrastructure enables the customization of therapies to meet individual patient needs. Advanced data analytics can help identify patient-specific factors and optimize treatment protocols, leading to more effective and personalized therapies.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-based platforms and digital MES provide the scalability and flexibility needed to adapt to changing market demands. Manufacturers can quickly scale up or down their operations, respond to new therapeutic developments, and efficiently manage production schedules.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: The integration of digital technologies allows for the collection and analysis of vast amounts of data. This data-driven approach can inform strategic decisions, optimize manufacturing processes, and improve overall operational efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance and Quality Assurance: Digital infrastructure ensures that all processes are documented and traceable, facilitating regulatory compliance. Automated quality control measures can maintain consistent product quality, reducing the risk of deviations and ensuring patient safety.
Enhancing the vial/vein-to-vein process with enterprise-level digital infrastructure is essential for the success of cell and gene therapies. By addressing the challenges of data management, coordination, and quality control, digital infrastructure can improve efficiency, traceability, and patient outcomes. The adoption of Industry 4.0 principles and advanced digital solutions will be critical in ensuring the safe and effective delivery of lifesaving therapies. As the CGT industry continues to grow, embracing these technologies will not only streamline operations but also pave the way for future innovations and personalized medicine. The integration of digital infrastructure is not just a technological upgrade; it is a strategic imperative that will shape the future of healthcare.
References
- Scaling Cell & Gene Therapies For The Healthcare Industry: Industry Requirements, Healthcare Personnel Perspective
- The Cell and Gene Therapy Consortium's Perspective on Harmonizing Data Collection for Patient Enrollment, Therapy Ordering and Scheduling, and Cell Collection - ScienceDirect
About The Author
 Alex Klarer founded the strategy consulting firm Engelex to provide deep, quantitative insights into and provide actionable strategies for manufacturing, technology development, and vial/vein-to-vein supply chain management. Klarer is an industry professional with a decade of experience in a variety of roles from process development, CMC, manufacturing engineering, cGMP manufacturing, technology development, market analysis, and corporate strategy. He held those roles at Genentech, Minaris Regenerative Medicine, and BioCentriq.
Alex Klarer founded the strategy consulting firm Engelex to provide deep, quantitative insights into and provide actionable strategies for manufacturing, technology development, and vial/vein-to-vein supply chain management. Klarer is an industry professional with a decade of experience in a variety of roles from process development, CMC, manufacturing engineering, cGMP manufacturing, technology development, market analysis, and corporate strategy. He held those roles at Genentech, Minaris Regenerative Medicine, and BioCentriq.