These Top 2022 Global Bioprocessing Trends Will Affect The Industry In 2023
By Shriya Bhatkhande, research associate, BioPlan Associates

As the biopharmaceutical industry recovers from the COVID-19 pandemic, it has demonstrated remarkable resilience in adapting to supply chain challenges, while still improving efficiency. Growth in the industry has been due to several factors. Certainly, COVID vaccines and therapeutic production have played a significant part. The 13 billion doses administered over the past two years have added to the industry’s total output. But much of the 24.5% increase in revenue from consumables and equipment reported this year in our 19th Annual Report and Survey of Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing Capacity and Production has been due to other factors. These include:
- Stockpiling to avoid supply problems and risks due to shortages.
- Reduction in discounting — because of supply challenges and increased demand, vendors have not discounted orders to large suppliers. This has resulted in higher revenue on the same volume of sales. We do note, however, that it appears vendors have not engaged in price gouging. For example, list prices in 2021 increased only around 5%.
In some segments, such as single-use devices, where demand has been very high, reported revenue growth rates have exceeded 35%, according to our study. But relative to the magnitude of the entire biologics industry, COVID-related projects continue to represent a relatively small share. If COVID-related projects take precedence, then the challenges to supply for non-COVID biologics can create unique demand situations.
Other global biomanufacturing trends continue to emerge during COVID, and these are outlined in our current report, which surveyed 144 decision makers from bioprocessing organizations and 134 suppliers to the industry in 25 countries. Just a few of the highlighted trends in this year's research include:
- Increased Efficiencies: Bioprocessing saw efficiency and productivity improvements as titer levels increased this year to an average of 2.92 g/L, up from 2.65 g/L in 2021 and 1.95 g/L in 2008.
- Lower Cost Per Gram For mAbs: In 2021, the average cost-per-gram was at its lowest point on record. The market has been expanding at a rate of 12% to 13% per year over the past decade, virtually doubling in size every five years. With this growth, efficiencies and economies of scale have resulted in lower unit costs. Cost savings from process automation and other factors continue to expand.
- Offshoring: International biomanufacturing and offshoring are growing, especially in major markets and Asia. An upcoming wave of facilities making biologics, COVID-19 treatments, as well as other pandemic and biodefense products, is increasing regional capacity, and growth among regional contract and development manufacturing organizations (CDMOs), especially in Asia, continues. The demand for biologics in these regions is also creating ready-made markets for innovative therapies. In-country manufacturing by CDMOs can create opportunities for foreign biopharmaceutical companies.
- Cell And Gene Therapy: The number of cell and gene therapy pipeline products and facilities, including commercial manufacturing, is increasing.
- Demand For Qualified Staff: Biopharmaceutical manufacturing is being challenged by the lack of qualified staff. Over 50% of the industry is having trouble finding qualified employees. This continues to get worse each year.
- Single-use Device Usage: Single-use technologies are accelerating their replacement of stainless steel. The reduction in new commercial stainless-steel-based processing continues.
- Contract Manufacturing On The Rise: The growth in contract manufacturing facilities means that biopharma manufacturers have more flexible options for their manufacturing strategies, including outsourcing their product manufacturing.
We detail below just a few of the key trends from this year’s study that will impact the industry in 2023.
Sales Growth Of Bioprocess Supplies And Services
COVID-19 has upended the supply side of the industry, and demand for most consumables has been unprecedented. However, in comparison, over the past 15 years, annual sales revenue for bioprocessing equipment, instrumentation, materials, services, and consumables had remained remarkably steady at around 14%. This consistency through recessions and boom periods occurred because the industry is relatively insulated from fluctuation. Derived demand for production of critical therapeutics ensures a stable industry segment. In addition, the steady pipeline for new clinical projects, the opening of new global geographies, and new modalities such as cell and gene therapies have created a safe space with consistent growth.
This all changed dramatically during COVID times. Revenue for all bioprocess supply and services areas increased significantly. While there has not been evidence of price gouging, on average, bioprocessing suppliers showed a 24.5% overall growth in sales. This is a 7-percentage-point increase from 2021. And over two years, there was nearly a doubling in revenue growth.
The most significant increase in revenue was for raw materials and consumables, which jumped to 27%. Contract manufacturing services revenues also increased, as did those for engineering, validation, and CROs. As we enter 2023, suppliers will likely continue to see demand exceed supply in many cases. However, industry demand, anecdotally, is moderating and is likely to return to pre-COVID levels soon. Much of this growth in revenue has been due to the elimination of discounts by suppliers, even for very large customers. Warehousing and stockpiling of excess inventory by end user companies has also continued by a significant percentage of end users, even as COVID production challenges diminish.
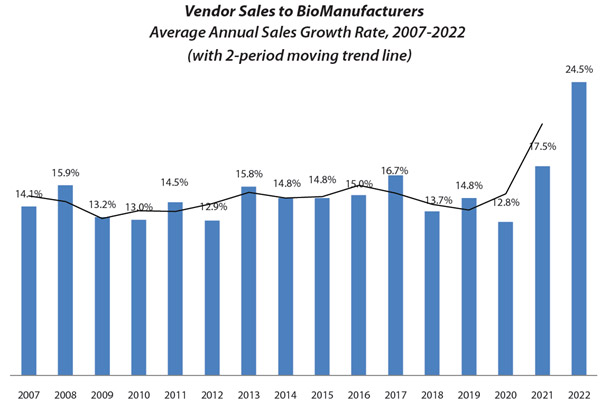
Source: 19th Annual Report and Survey of Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing, April 2022, BioPlan Associates, Inc.
Figure 1: Growth in vendor sales for biologics (2018-22)
Impact Of COVID-19 On The Supply Chain
COVID-19 changed the landscape of our industry, and although supply shortages have seemed to ease up a bit over the past two years, we're still experiencing plenty of challenges. Overall, supply shortages continue to rise. Manufacturers have been challenged with getting raw materials to produce enough products. Because of the problems a shortage can bring a manufacturer, the fear of not having access to their supplies is impacting the entire segment. With vaccines and COVID therapeutics taking priority over other drugs, some disruptions are expected to continue at least into next year.
To cope with this growth, vendors are developing alternative channels and validating new suppliers. This is creating an entirely new competitive environment. Secondary and even tertiary suppliers are being added as approved vendors, just to ensure supply chain integrity. These new suppliers are also beginning to take bites of the market share otherwise held by more established suppliers. In three to five years, these smaller vendors likely will take a greater share, and we will start to see additional mergers and consolidations in the supply segment.
Five-Year Predicted Capacity Constraints Decrease Despite COVID-19
Our annual report data shows that the trend for future capacity constraints continues downward. Furthermore, the expectation that industry respondents will see no capacity constraints over the next five years is about the same as the previous year, with an average of 20% for the past five years.
Essentially, it appears COVID-19 is not going to have a significant impact on bioprocessing capacity over the next five years. This trend reflects the industry's increasing competence in capacity management, even during a pandemic period. Further, the COVID bump was directly felt by only a handful of vaccines manufacturers. The downstream effect on the industry, especially for CDMOs, however, was dramatic. While larger CDMOs were busy with COVID projects, certain big non-COVID projects were being given to mid-tier CDMOs, who in turn found themselves capacity-constrained and refusing or delaying smaller projects, which then continued downstream to yet smaller CDMOs.
With experience, industry operators have proven they can generally meet ever-increasing future demands by using existing equipment and capacity, bringing more flexible single-use systems online, leveraging contract manufacturing capacity, and using modular construction techniques to speed timelines.
Capacity constraint projections for future years remain murky. Industry response to the pandemic has resulted in increased vaccine production, which may possibly contribute to a capacity glut that could be difficult to manage in the near term.
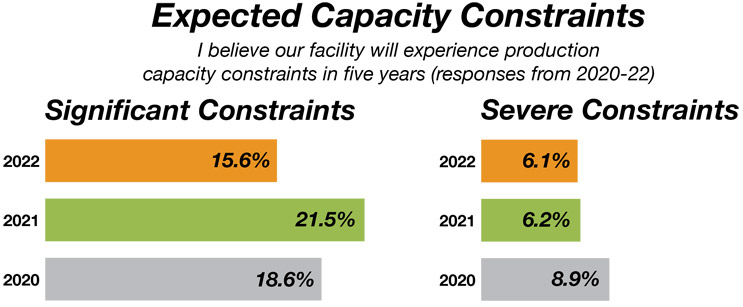
Source: 19th Annual Report and Survey of Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing, April 2022, BioPlan Associates, Inc.
Figure 2: Projected capacity constraints in five years, 2020-22
Inability To Hire And Retain Experienced Staff Creates Capacity Constraints
Staffing is creating more of a capacity bottleneck than bricks-and-mortar facilities. While factors including supply chain and physical facility issues have continued to rise this year, a lack of experienced technical and production staff is having an even greater effect.
Respondents were asked to identify which major constraining factors limited their organization's growth. We found 34.2% answered, “The inability to hire new, experienced technical and production staff.” Another finding we saw this year was an inability to retain experienced scientific staff, which increased by 13.3 percentage points (32.5% in 2022 vs. 19.2% in 2021). In addition, the concern for retention of experienced technical and production staff increased by 10 percentage points from 2021 to 2022.
Scientific and manufacturing staff can be tough to keep around, with experienced professionals retiring and a growing demand for bioprocessing specialists in the industry. On top of that, new advances like cellular therapy are adding to the need for experienced employees.
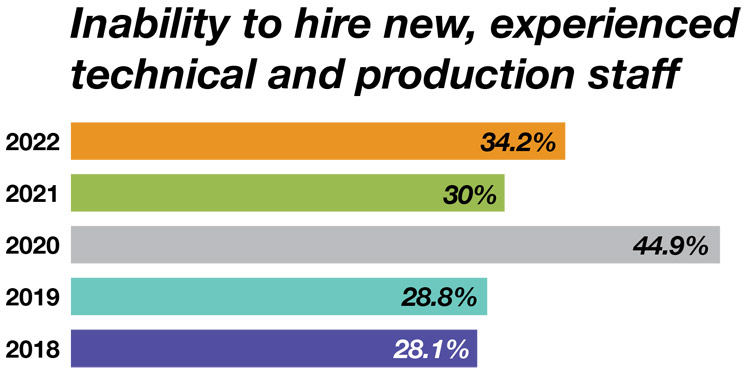
Source: 19th Annual Report and Survey of Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing, April 2022, BioPlan Associates, Inc.
Figure 3: Selected factors likely to create capacity constraints over five years (responses from 2008-22)
Demand For More Cellular And Gene Therapy Expertise
For 2022, we saw that the percentage of facilities having capacity constraint problems, “Hiring more staff with cell/gene therapy manufacturing expertise," is nearly 20% higher than in 2021. This trend will likely be even more important for larger facilities or those that want to work on a commercial scale. Facilities in this range often need the most qualified individuals to grow and succeed, so it's important to hire not just for quantity but for quality, too.
BioPlan publications have noted staffing shortages in the cellular and gene therapy sectors for years. Rapid growth in these areas make it challenging to find skilled applicants. Continued growth in the biopharmaceutical industry and rapid expansion in COVID vaccine areas are quickly taking many qualified staff that otherwise might be working on these projects.
U.S. And China Top International Outsourcing Destinations
Outsourcing has continued to grow as access to in-house expertise has tightened. Some of this outsourcing is being directed outside the sponsor’s country. This international offshoring of biologics activities, including production, has continued to grow over the 19 years we have surveyed the industry. We sought to identify trends in this offshoring to understand facilities' plans for international capacity expansion over the next five years. For non-U.S.-based respondents, 39.6% indicated that the U.S. would be a “strong likelihood” or “likelihood” for outsourcing production.
This year, China moved to the No. 2 spot, with 33.7% of respondents, up from No. 10 in 2021. Among U.S. respondents specifically, China is now the No. 1 "possible" outsourcing destination, with 47.8%. We see a large increase in respondents considering China a potential production outsourced location.
COVID-19 is accelerating the trend in which major biologics innovators see CMOs in developing regions as viable partners. While it will likely take years for most biologics CMOs in India, China, Brazil, and other developing countries to meet full cGMP standards, and to be accepted as high-quality biopharmaceutical manufacturers, examples such as WuXi Biologics in China have achieved rapid success and rank among the top five global CMOs. Further, as Western biologics innovators continue to enter these emerging markets, partnering with domestic CDMOs can be a logical strategy. This has created a sub-market where certain CDMOs are being considered by major sponsors and innovators as viable options for new market entry.
Outsourcing Of Biologics Is On The Rise
When asked to estimate the percentage of production they plan to outsource over the next five years, our respondents over the past 16 years have shown fairly consistent behavior. The long-term trend has been toward less in-house production and more outsourcing of at least some of a facility’s operations. Today, we see this trend for all major platforms including mammalian cell culture and microbial fermentation. For mammalian cell culture, for example, the percentage of respondents doing 100% in-house production has continued to decline steadily from 57.6% in 2006 to 34.9% this year. Conversely, 65.1% of respondents are outsourcing some of their production.
And it looks likely that this will continue. Mammalian cell culture facilities report they are expecting an even higher level of outsourcing in 2027, with 78.7% of respondents planning on outsourcing at least some production by then.
Globally, the trend has been decreasing since 2006, indicating that more facilities rely on external service providers. CDMOs add flexibility and they have production capabilities and experienced staff that their clients may not have.
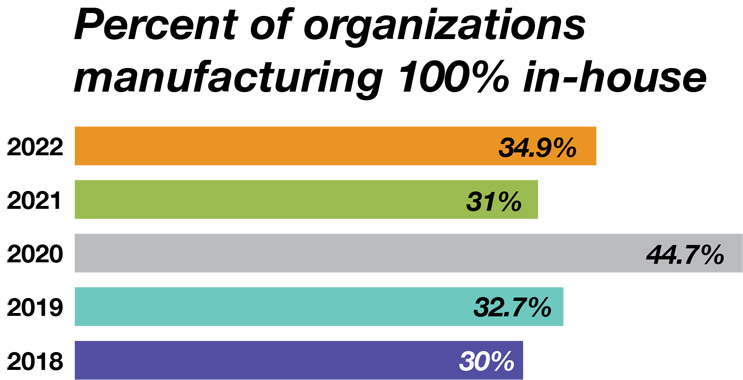
Source: 19th Annual Report and Survey of Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing, April 2022, BioPlan Associates, Inc.
Figure 4: Percent of facilities manufacturing 100% of their biologics in-house (2006-22)
Summary of results from BioPlan Associates’ 19th Annual Report and Survey of Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing Capacity and Production
Participate In The 20th Annual Report And Survey
BioPlan Associates is surveying the industry for its 20th annual report and survey, to be published in 2023. The survey benchmarks current global and regional trends affecting the bioindustry. Click here to take the survey.
About The Author:
 Shriya Bhatkhande holds a Master’s in biotechnology and business from University College, Dublin, and a Master’s degree in food science and technology. Her background includes strategy and business development for Cambridge Life Sciences, U.K., and Inflection Biosciences, Dublin. She’s done extensive research and industrial analysis on a range of products from the design phase through product. Reach her at sbhatkhande@bioplanassociates, www.bioplanassociates.com.
Shriya Bhatkhande holds a Master’s in biotechnology and business from University College, Dublin, and a Master’s degree in food science and technology. Her background includes strategy and business development for Cambridge Life Sciences, U.K., and Inflection Biosciences, Dublin. She’s done extensive research and industrial analysis on a range of products from the design phase through product. Reach her at sbhatkhande@bioplanassociates, www.bioplanassociates.com.
