RNA Therapeutics: New Market Research
By Pooja Sharma, Global Market Insights

In addition to vaccines, RNA-based therapies are gaining traction for their promise in targeting cancers, genetic disorders, and rare diseases. According to our new market research, the RNA therapeutics industry is predicted to exceed $31 billion by 2032, exhibiting a 5.7% CAGR over 2024–2032. This article shares key findings and trends from our market research.
The Role Of Vaccines In The RNA Therapeutics Market
RNA-based vaccines represent one of the most significant milestones in modern therapeutics. Unlike traditional vaccines that use inactivated or attenuated pathogens, RNA vaccines introduce genetic material encoding an antigen, which then stimulates the immune system to produce a protective response. This approach has garnered attention for its versatility and speed, as seen in the rapid development of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines.
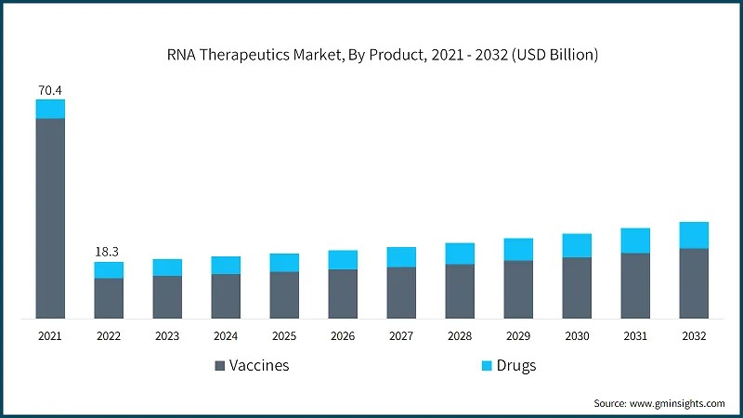
The success of mRNA vaccines, notably those produced by Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech, has proven that RNA-based platforms can be highly effective. These vaccines have been instrumental in curbing the COVID-19 pandemic, setting a precedent for future vaccine development. The high efficacy rates of these vaccines, often above 90%, coupled with a relatively swift development process, have opened doors for new applications in infectious diseases, oncology, and personalized medicine.
Against this backdrop, in August 2024, Eli Lilly and Company launched the Lilly Seaport Innovation Center, an advanced R&D hub located in Boston's Seaport district. The center aims to advance Eli Lilly's efforts in RNA and DNA-based therapies and drive the discovery of new drug targets for diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases.
mRNA: Dominating The RNA Therapeutics Landscape
mRNA has emerged as the most prominent type of RNA therapeutic due to its versatile applications and relative ease of production. In addition to vaccines, mRNA is being explored for its potential to produce therapeutic proteins within the body, enabling treatments for a wide range of diseases.
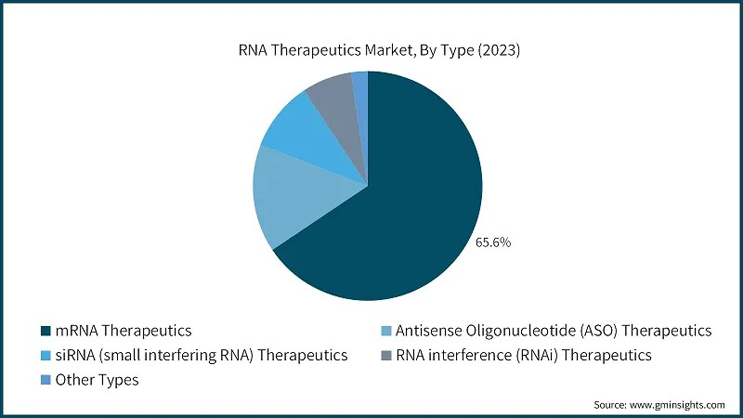
The scope of mRNA therapeutics is expanding beyond infectious diseases. Recent studies indicate potential applications in cancer immunotherapy, where mRNA can be tailored to encode antigens specific to a patient's tumor cells. BioNTech and Moderna, pioneers of mRNA technology, are actively working on personalized cancer vaccines designed to stimulate a patient-specific immune response against cancer cells.
For example, in September 2024, a new cancer vaccine developed by Moderna Pharmaceuticals demonstrated promising outcomes in early trials, bringing renewed optimism to cancer treatment. Using mRNA technology similar to that of COVID-19 vaccines, the vaccine — mRNA-4359 — trains the immune system to identify and eliminate cancer cells by differentiating them from healthy cells. In a Phase 1e clinical trial with 19 participants suffering from advanced solid tumors, eight patients showed no tumor growth, and no new tumors emerged during the study. Patients tolerated the vaccine well, and no severe side effects were reported. This promising approach indicates the potential of mRNA to revolutionize cancer treatment, offering a safer and less invasive alternative to chemotherapy and radiation.
Infectious Diseases: The Primary Indication Driving RNA Therapeutics
While oncology is a fast-emerging area, infectious diseases remain the primary focus for RNA therapeutics, especially in light of global challenges posed by pathogens like SARS-CoV-2, influenza, and emerging zoonotic viruses.
The flexibility of RNA platforms makes them ideally suited for infectious disease outbreaks. The National Institutes of Health reports that infectious diseases continue to be a major cause of illness and death globally, responsible for over 52 million deaths annually, or roughly 33% of total deaths worldwide. Nearly half of the global population remains vulnerable to emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. Recent data estimates around 14 million deaths in children under the age of 5 each year, with 70% attributed to vaccine-preventable diseases and 99% of these deaths occurring in developing countries.
Traditional vaccine platforms often take years to develop, while RNA vaccines can be adapted rapidly to match pathogen mutations. For example, mRNA-based flu vaccines are under development, potentially offering a more effective approach than conventional flu vaccines by targeting multiple strains with a single formulation.
Additionally, research on RNA-based therapies for other infectious diseases, such as HIV and Ebola, is gaining traction. A report from the Journal of Infectious Diseases (2023) suggests that RNA vaccines may offer a viable solution for endemic diseases in developing regions where infectious disease rates are high. By leveraging RNA technologies, healthcare systems may reduce the time and cost of delivering vaccines to populations in need.
North America: Leading The RNA Therapeutics Market
North America, particularly the U.S., is a global leader in RNA therapeutics, accounting for the largest share of research funding, clinical trials, and market revenues. The U.S. government's active support, through initiatives like Operation Warp Speed, has significantly boosted the development of RNA vaccines, making the region a powerhouse in the RNA market.
In February 2024, the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) awarded over $12.7 million to nine research teams to explore the vast potential of RNA in biotechnology applications, ranging from crop disease prevention to cancer therapies. Each team will receive between $1 million and $1.65 million through NSF’s Molecular Foundations for Biotechnology (MFB) program, a collaborative initiative with the National Institutes of Health’s National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI). NHGRI is also planning additional investments in RNA biology projects, with new funding announcements expected later in 2024 to support the development of innovative research technologies.
North America’s dominance can be attributed to its robust R&D infrastructure, well-defined regulatory framework, and substantial public and private investments. The FDA has demonstrated a streamlined approach for RNA therapeutics, particularly for vaccines, which has encouraged companies to accelerate their clinical programs. With the success of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, the regulatory pathway for RNA-based therapies has become clearer, reducing the timeline from development to market.
U.S. Hospitals Are Driving Greater RNA Therapeutics Adoption
In the U.S., hospitals are increasingly incorporating RNA-based treatments into their protocols, with many major health institutions conducting clinical trials for mRNA vaccines targeting a variety of conditions. Hospitals’ role in facilitating clinical trials and administering newly approved therapies is crucial in bridging the gap between research and patient care.
Hospitals are also partnering with biopharmaceutical companies to refine treatment administration and expand patient access to RNA therapies. This collaboration could streamline RNA therapeutic adoption and ensure a consistent supply chain, accelerating treatment availability for critical conditions.
Collaborative Efforts And Innovation Hubs
Biopharma giants such as Moderna, Pfizer, and BioNTech have established R&D hubs across the U.S., collaborating with academic institutions and research centers to drive innovation.
For instance, in February 2023, Moderna announced a partnership with Life Edit Therapeutics to combine Moderna's mRNA platform with Life Edit's proprietary gene editing technologies, including DNA base editors and RNA-guided nucleases (RGNs). Under the agreement, the companies will collaborate on research and preclinical studies, funded by Moderna.
Similarly, in July 2024, BioNTech and Triastek initiated a research partnership and platform technology licensing agreement to develop 3D-printed oral RNA therapeutics. This collaboration will focus on creating orally deliverable RNA treatments utilizing 3D printing technology, leveraging Triastek’s expertise in innovative tablet designs. These advanced designs aim to optimize RNA delivery across the gastrointestinal mucosa, reduce degradation within the gastrointestinal tract, and target the regions with the highest potential for therapeutic absorption.
In September 2024, Eli Lilly entered a major AI-driven drug discovery partnership with Genetic Leap, an RNA-focused biotech, in a deal valued up to $409 million through up-front and milestone payments. Genetic Leap, based in New York, utilizes AI models to identify RNA-targeted drugs, including innovative approaches to address traditionally undruggable targets. Through this collaboration, Lilly will select priority targets, while Genetic Leap will develop oligonucleotide drug candidates using its advanced AI RNA-targeting platform.
The establishment of biotech clusters in cities like Boston and San Francisco further reinforces North America’s leadership in RNA research and development. These collaborations aim to develop next-generation RNA platforms capable of tackling not only infectious diseases but also cancer, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular diseases.
Key Challenges And Opportunities In The RNA Therapeutics Market
While the RNA therapeutics market is proliferating, certain challenges must be addressed to unlock its full potential:
- Delivery Mechanisms: Efficient and targeted delivery remains a challenge for RNA therapeutics. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have been successful in mRNA vaccine delivery, but alternative methods are being explored for more targeted approaches.
- Manufacturing and Scalability: High manufacturing costs and scalability create barriers to widespread adoption. Industry players are working on improving manufacturing efficiency to bring down costs.
- Regulatory Landscape: As RNA therapeutics are relatively new, regulatory bodies are still developing frameworks to address their unique characteristics and potential long-term effects.
Despite these challenges, RNA therapeutics offer a promising frontier in medicine, with vast applications across therapeutic areas and the potential to revolutionize patient care.
Key Companies
The foremost players operating in the RNA therapeutics industry are:
- Alnylam Pharmaceuticals
- Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals
- BioNTech SE
- Ionis Pharmaceuticals
- Moderna
- Novartis AG
- Orna Therapeutics Pfizer
- Sanofi
- Sarepta Therapeutics
Conclusion
The RNA therapeutics market is a transformative force in healthcare, with broad applications that promise to reshape the treatment landscape for infectious diseases, cancer, and more. The versatility of RNA technologies, especially mRNA, has enabled rapid responses to health crises, exemplified by the COVID-19 pandemic, and unlocked new possibilities for personalized medicine.
As the demand for RNA therapeutics grows, driven by innovations in vaccine development, gene therapy, and regenerative medicine, North America’s leading role will be crucial. With a supportive regulatory framework, advanced research facilities, and a commitment to advancing patient care, the region is poised to remain at the forefront of this dynamic market.
Investments in R&D, collaborations across the biotech industry, and advancements in delivery technologies will further strengthen the RNA therapeutics landscape. For industry stakeholders, staying ahead of regulatory trends and investing in new delivery and manufacturing technologies will be essential to capitalize on the opportunities in this expanding market.
