Lean Manufacturing Implementation In Pharmaceutical Injectable Facilities
By Ashok Kumar Dasari, Viatris BLR India

While lean manufacturing offers transformational benefits for pharmaceutical injectable facilities, successful implementation requires sophisticated navigation of unique industry challenges. This comprehensive analysis examines implementation disadvantages, practical challenges, and evidence-based solutions derived from real-world experiences across leading pharmaceutical organizations. The framework presented enables systematic risk mitigation while maximizing implementation success probability.
Implementation Disadvantages And Inherent Challenges
1. Regulatory Compliance Complexity: The Documentation Dilemma
The pharmaceutical industry's extensive documentation requirements and rigorous change control protocols can create apparent conflicts with lean principles aimed at eliminating non-value-added activities. This fundamental tension requires sophisticated resolution strategies.

Case Study: Company X’s Implementation Failure: A major pharmaceutical manufacturer attempted aggressive documentation reduction as part of its lean initiative, resulting in FDA observations during inspection. The remediation required 18 months and $3.2 million investment to restore compliance, demonstrating the critical importance of balanced approaches.
2. Capital Investment Requirements and Extended ROI Timelines
Lean manufacturing implementation demands significant up-front investments across multiple categories, with returns materializing over extended time frames that challenge traditional pharmaceutical business models.
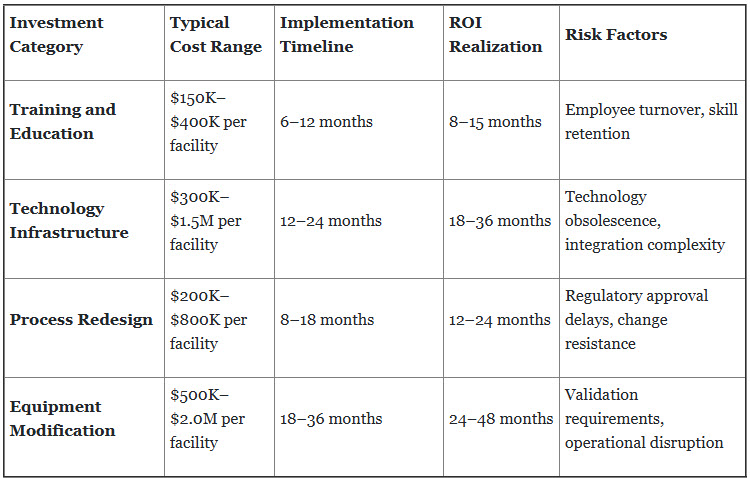
Financial Impact Analysis: Organizations typically require two to three years to achieve full ROI realization, creating cash flow challenges and executive pressure for premature implementation acceleration.
3. Cultural Resistance and Organizational Inertia
Pharmaceutical manufacturing cultures historically emphasize procedural compliance over operational efficiency, creating substantial resistance to lean transformation initiatives that challenge established practices.
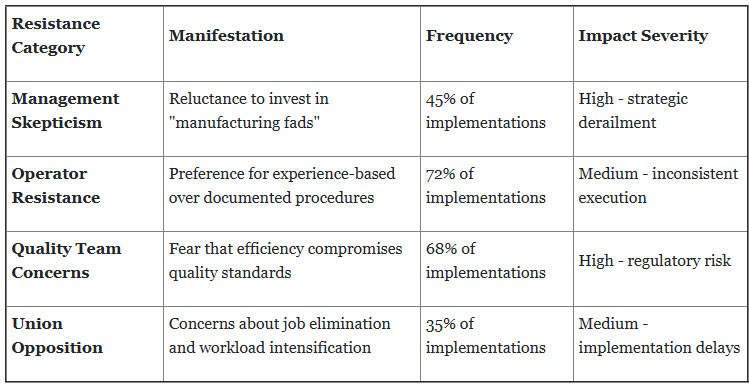
Detailed Example: GSK Cultural Transformation: GSK's Singapore facility initially faced 78% employee resistance to standardized work procedures. Senior operators with 15+ years’ experience insisted their empirical methods were superior to documented standards. This resistance led to:
- a six-month implementation delay
- $400K in additional training costs
- a 23% temporary productivity decline
- inter-departmental conflicts requiring executive intervention.
Resolution: Through comprehensive change management including employee champions, skills-based recognition, and continuous feedback integration, GSK achieved 89% employee buy-in within 18 months.
4. Supply Chain Vulnerability and Risk Amplification
Just-in-time principles can increase vulnerability to supply chain disruptions, creating particular concerns for critical injectable medications where stockouts directly impact patient care.
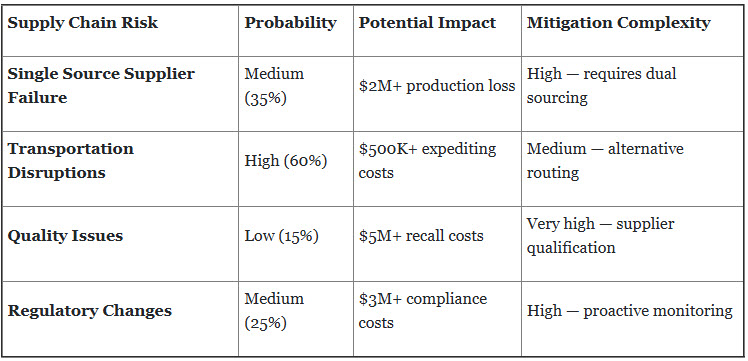
Critical Case Study — Supply Chain Disruption: A leading injectable manufacturer experienced a three-week production shutdown when their single-source API supplier encountered quality issues. The impact included:
- $12 million in lost production
- $2.3 million in expediting costs for alternative suppliers
- six-month customer delivery delays
- potential product shortage impacting patient care.
Practical Implementation Challenges with Quantified Solutions
1. Documentation Management System Failures
Challenge Magnitude: Sixty-eight percent of pharmaceutical facilities experience significant productivity losses due to inadequate document control systems, with personnel spending two to three hours per shift searching for current procedures.

Comprehensive Solution Implementation:
Takeda's Transformation: Takeda's Osaka facility implemented a comprehensive eDMS solution that achieved:
- 75% reduction in document search time
- 99.2% version control accuracy
- $650K annual productivity savings
- zero documentation-related audit findings.
Technology Solution Framework:
- Phase 1 (0–3 months): System selection and basic configuration
- Phase 2 (3–9 months): Document migration and workflow automation
- Phase 3 (9–12 months): Mobile integration and advanced analytics
- Phase 4 (12+ months): Continuous optimization and AI integration
2. Activity Planning and Scheduling Optimization Failures
Challenge Analysis: Inefficient coordination of routine maintenance, cleaning validation, and changeover activities creates bottlenecks while wasting valuable cleanroom operational time.
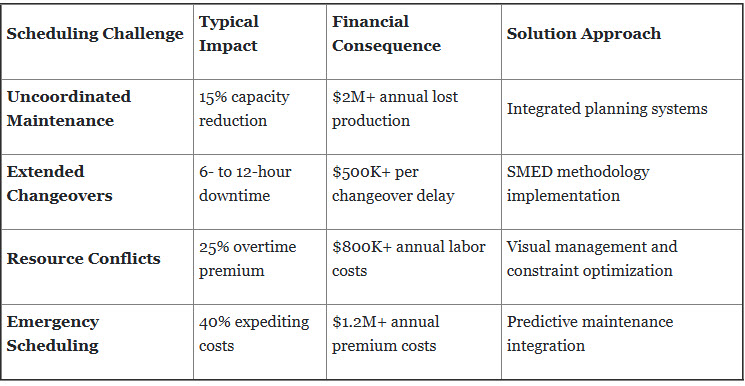
Detailed Implementation Example:
Bristol Myers Squibb's Scheduling Revolution: BMS's facility experienced chronic scheduling inefficiencies until implementing their integrated planning solution:
Problem State:
- Maintenance and production teams worked independently.
- Equipment downtime occurred during prime production hours.
- There was a 15% reduction in available manufacturing time.
- The company saw a $2.1 million annual impact from scheduling conflicts.
Solution Implementation:
- Technology Integration: Advanced scheduling software with constraint-based optimization
- Process Redesign: Cross-functional planning teams with weekly coordination meetings
- Visual Management: Real-time dashboards showing resource utilization and conflicts
- Performance Metrics: Equipment utilization, schedule adherence, and conflict resolution time
Results Achieved:
- 22% improvement in equipment utilization
- 85% reduction in scheduling conflicts
- $1.8M annual savings from optimized resource allocation
- 97% schedule adherence rate
3. Workplace Organization and 5S Implementation Failures
Challenge Scope: Poor workplace organization creates extended search times, increases safety risks, and reduces operational efficiency within sterile manufacturing environments.
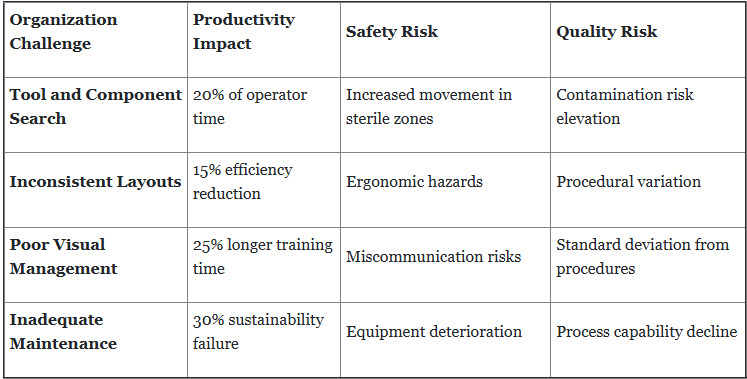
Comprehensive 5S Solution Framework:
Case Study — Catalent's 5S Excellence: Catalent's sterile facility transformation demonstrates systematic 5S implementation:
Implementation Phases:
- Sort (Seiri) — Months 1–2:
- red tag events removing unnecessary items
- 40% reduction in workspace clutter
- $75K value recovered from unused inventory.
- Set in Order (Seiton) — Months 2–4:
- standardized locations with visual indicators
- tool shadowing and component mapping
- 60% reduction in search time.
- Shine (Seiso) — Months 3–5:
- daily cleaning standards and checklists
- equipment condition monitoring integration
- 25% improvement in equipment reliability
- Standardize (Seiketsu) — Months 4–8:
- documented procedures and audit systems
- digital checklists and compliance tracking
- 95% audit compliance achievement.
- Sustain (Shitsuke) — Months 6–12:
- cultural integration and recognition programs
- continuous improvement and employee suggestions
- 92% long-term sustainability rate.
Quantified Results:
- 65% reduction in material search time
- 40% improvement in workspace efficiency
- 99.3% contamination prevention compliance
- $450K annual productivity improvement.
Strategic Solutions And Implementation Frameworks
1. Comprehensive Change Management Strategy
Successful lean transformation requires sophisticated change management approaches that address human, cultural, and organizational dimensions simultaneously.
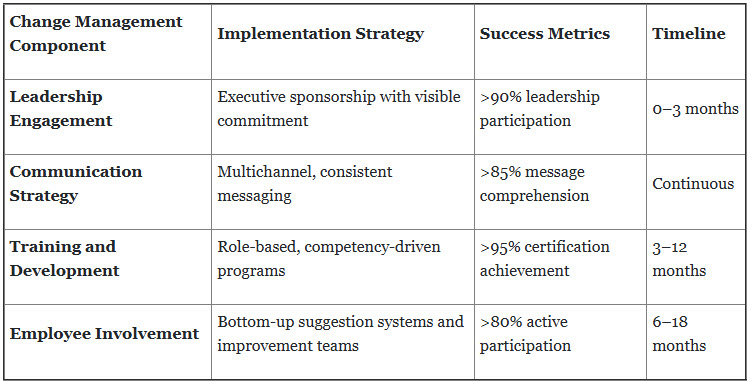
Proven Implementation Model — Roche's Change Excellence:
Foundation Phase (0–6 months):
- Executive leadership alignment and visible commitment
- Change champion network establishment across all departments
- Comprehensive communication strategy with regular updates
- Initial training programs for key stakeholders
Acceleration Phase (6–18 months):
- Department-specific implementation teams
- Regular success story sharing and recognition programs
- Continuous feedback collection and response systems
- Advanced skills development and certification programs
Sustainment Phase (18+ months):
- Performance management system integration
- Continuous improvement culture embedding
- Long-term incentive alignment with lean objectives
- Knowledge management and best practice sharing
Results Achieved:
- 87% employee engagement scores (15-point improvement)
- 94% training completion rate within target time frames
- 340+ employee-generated improvement suggestions implemented
- Zero involuntary turnover during transformation period.
2. Technology Integration and Digital Enablement
Strategic technology integration accelerates lean implementation while providing sustainable competitive advantages through advanced capabilities.

Technology Implementation Success Story — Merck's Digital Transformation:
Challenge: Merck's Ireland facility needed to optimize aseptic filling operations while maintaining regulatory compliance and improving productivity.
Solution Architecture:
- Digital Twin Development: Complete virtual replica of filling line operations
- Real-Time Monitoring: 200+ sensor integration for environmental and process parameters
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning algorithms for failure prediction
- Mobile Integration: Operator access to real-time information and procedures
Implementation Timeline:
- Phase 1 (0-6 months): Infrastructure development and sensor deployment
- Phase 2 (6-12 months): Digital twin creation and initial algorithm development
- Phase 3 (12-18 months): Predictive model training and validation
- Phase 4 (18-24 months): Full integration and optimization
Quantified Results:
- 15% capacity increase without additional equipment
- 28% reduction in unplanned downtime
- 35% improvement in changeover efficiency
- $2.1 million annual savings from optimized operations.
3. Risk Management and Mitigation Strategies
Comprehensive risk management ensures successful lean implementation while protecting critical business operations and regulatory compliance.

Disclaimer: The information provided in this document is intended for general informational purposes only. The details and company names mentioned herein have been sourced from various social media platforms and internet resources. While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the information, the author does not guarantee its completeness or reliability. The author shall not be held liable for any errors, omissions, or any outcomes related to the use of this information.
About The Author:
 Ashok Kumar Dasari is a life science professional at Viatris BLR India. He is a seasoned biopharmaceutical professional with extensive expertise in pharmaceutical practices, aseptic operations, regulatory compliance, and total quality management systems. With a career that spans both local and international landscapes, he has consistently worked to address the evolving challenges of the modern pharmaceutical industry. Dedicated to lifelong learning and knowledge sharing, he remains committed to writing on novel topics in the pharmaceutical domain and beyond, offering narratives that inform, inspire, and innovate.
Ashok Kumar Dasari is a life science professional at Viatris BLR India. He is a seasoned biopharmaceutical professional with extensive expertise in pharmaceutical practices, aseptic operations, regulatory compliance, and total quality management systems. With a career that spans both local and international landscapes, he has consistently worked to address the evolving challenges of the modern pharmaceutical industry. Dedicated to lifelong learning and knowledge sharing, he remains committed to writing on novel topics in the pharmaceutical domain and beyond, offering narratives that inform, inspire, and innovate.
