Quality Imperatives In Oral Solid Dosage Manufacturing: An Overview
By Padmini Ayapilla, Freyr Solutions

Oral solid dosage (OSD) manufacturing is a multifaceted process based on adherence to stringent regulatory guidelines, efficient workflow management, and uncompromising quality control measures. This article delves into the critical aspects of OSD manufacturing and the importance of understanding and implementing regulatory guidelines within the context of quality. It also explores the key considerations for manufacturing, emphasizing the need for a clear description of the process, technical justifications for any changes, and a comparative analysis of approved versus proposed processes.
The critical aspects of OSD manufacturing include:
- Chemical Documentation: This involves detailed information on the chemical properties of the drug substance, excipients, and the final product. It is essential to ensure that any changes in the chemical composition do not adversely affect the product's safety, efficacy, or quality.
- Manufacturing and Controls: Changes in the manufacturing process, equipment, or site can impact the product's quality. Maintaining stringent controls and validating any changes to the manufacturing process are crucial to ensure consistent product quality.
- In-vitro Dissolution Testing: This testing is critical to ensure that the drug’s release from the OSD is consistent and within specified parameters. Any changes to the formulation or manufacturing process that could affect dissolution rates must be thoroughly tested.
- In-vivo Bioequivalence: When changes are made to an OSD, it is necessary to demonstrate that the modified product is bioequivalent to the original product. This means the product must show the same bioavailability and therapeutic effect.
Key Regulatory Guidelines For OSD
- SUPAC-IR (scale-up and post-approval changes for immediate release solid oral dosage forms): This guidance provides a framework for managing changes in components, composition, manufacturing sites, batch sizes, and manufacturing processes for immediate release OSDs.
- SUPAC-MR (scale-up and post-approval changes for modified release solid oral dosage forms): Like the SUPAC-IR, this guidance addresses post-approval changes for modified release OSDs, including chemistry, manufacturing, and controls; in vitro dissolution testing; and in vivo bioequivalence documentation.
- Quality System Guidances, such as:
- Pharmaceutical Quality System/Quality System Guidances Guidance for Industry Quality Systems Approach to Pharmaceutical CGMP Regulations (September 2006).
- Guidance for industry Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms: Scale-Up and Post-approval Changes: Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls, In Vitro Dissolution Testing, and In Vivo Bioequivalence Documentation (November 1995).
- Guidance for industry Nonsterile Semisolid Dosage Forms: Scale-Up and Post-approval Changes: Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls; In Vitro Release Testing and In Vivo Bioequivalence Documentation (May 1997).
- Guidance for Industry, Process Validation: General Principles and Practices (FDA, January 2011).
- Dissolution Testing of Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms (FDA, 1997).
- FDA's Quality Systems Approach to Pharmaceutical cGMP Regulations (October 2006).
- Process Validation, such as:
- ASEAN Guidelines for Validation of Analytical Procedures.
- Current pharmacopoeias (e.g., United States Pharmacopoeia, European Pharmacopoeia, and Japanese Pharmacopoeia).
- FDA Guidance for Industry, Process Validation: General Principles and Practices.
- Health Canada's guidelines and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations.
- ICH Guidelines: The International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) provides several guidelines relevant to OSD manufacturing, including Q8(R2), Pharmaceutical Development, Q7, Good Manufacturing Practice for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, and others that may apply depending on the specific changes.
It is important to consult the most recent versions of these guidelines and to engage with regulatory authorities early in the process of making changes to ensure compliance and facilitate a smooth approval process.
Production Management in OSD Manufacturing
A series of structured activities and processes is necessary to ensure that the production of tablets, capsules, and powders is carried out efficiently, safely, and in compliance with regulatory standards. Here are key aspects of workflow management in OSD manufacturing:
- Batch Formula Management: The batch formula must be well defined before manufacturing begins. This includes listing all dosage form components, with their amounts on a per-batch basis. This ensures consistency and traceability in production.
- Process Validation: A validation scheme should be followed to confirm that the manufacturing process produces a product meeting its predetermined specifications. This includes:
- Design Qualification (DQ): Ensure the design of the manufacturing process is suitable for its intended purpose.
- Installation Qualification (IQ): Verify that equipment and systems are installed correctly.
- Operational Qualification (OQ): Ensure the equipment and systems operate according to their operational specifications.
- Performance Qualification (PQ): Provide documented verification that the entire process operates within the anticipated operating ranges..
- Dust Control and Cross-contamination: Special attention is required in the design, maintenance, and use of premises and equipment to control dust and prevent cross-contamination, which is critical in OSD manufacturing.
- Pressure Cascade and Air Handling: Implement a pressure cascade system to ensure that air flows from areas of higher pressure to lower pressure, maintaining cleanroom standards and preventing contamination.
- Point Extraction: Use point extraction systems to remove dust and maintain air quality, with the extraction point located as close as possible to the source of the dust.
- Equipment and Facility Design: Design equipment and facilities to facilitate easy cleaning, maintenance, and efficient workflow. This includes the use of pass-through hatches or pass boxes to maintain segregation and pressure differentials between different manufacturing zones.
- Manufacturing Process Development: Optimize the manufacturing process, including critical process parameters, to ensure consistent product quality. This involves understanding the impact of process changes on product performance and ensuring that any differences between clinical and commercial batches are well understood and justified.
- Quality Control and Specifications: Establish release and shelf-life specifications for the OSD product, including in-process controls, dissolution profile testing, and ensuring that the product meets all quality criteria throughout its shelf life.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintain thorough documentation, including batch records, validation reports, and change control records, to ensure traceability and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhere to guidelines and regulations set forth by regulatory bodies such as the U.S. FDA, including SUPAC guidelines for IR (immediate release) and MR (modified release) solid oral dosage forms, and ASEAN guidelines for manufacturing process validation.
- Continuous Improvement: Implementing a system for continuous monitoring and improvement of the manufacturing process, including quality by design (QbD) principles and risk management strategies.
Comparative Analysis Of Approved Versus Proposed OSD Manufacturing Processes
In the pursuit of innovation and optimization within OSD manufacturing, it's imperative to adhere to stringent regulatory guidelines while striving for enhanced efficiency and quality. Here's a table that demonstrates the comparison between the approved and proposed manufacturing processes:
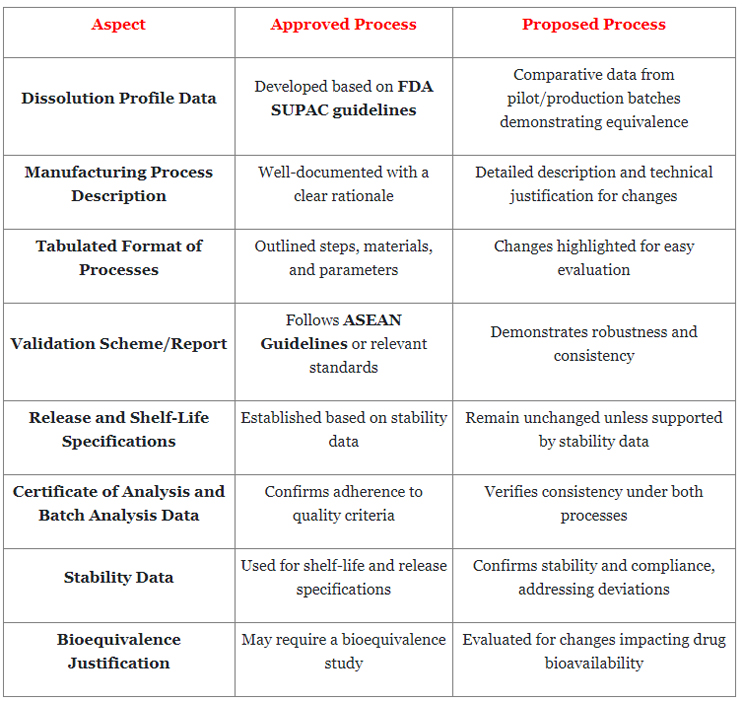
To summarize, manufacturing OSD forms requires rigorous adherence to regulatory guidelines, meticulous workflow management, and unwavering commitment to quality control. This article highlights critical aspects of OSD manufacturing, including regulatory compliance, workflow considerations, and quality imperatives. By adhering to guidelines such as the SUPAC and ASEAN and prioritizing factors like batch formula management and process validation, manufacturers can ensure the safe and effective delivery of medications to patients worldwide.
 About The Author:
About The Author:
Padmini Ayapilla is team lead, Medicinal Products Regulatory Division, at Freyr Solutions. She holds extensive experience in regulatory affairs, drug labeling, and publishing and submissions.
